Trading natural gas offers a unique opportunity to capitalize on one of the world’s most important renewable energy sources. Primarily used for essential needs like heating, cooking, and electricity, NG is among the most basic commodities on the planet. And, as demand for cleaner energy grows, natural gas has become a crucial component in the global energy transition.
If you plan to trade natural gas, you must first understand how this market works. No matter what your trading goals are, understanding the fundamentals of natural gas trading is key to navigating its volatility and making informed decisions.
In this article, we’ll cover how to trade natural gas, from the basics to advanced strategies. You’ll learn about the factors that drive natural gas prices, key reports to monitor, and how to apply technical analysis to find trading opportunities. By the end, you’ll be ready to confidently approach the natural gas market.
- Natural gas is a key player in the transition to cleaner energy, with increasing demand from both industrial usage and the transportation sector.
- Natural gas prices are highly volatile, influenced by factors like seasonal weather patterns, geopolitical events, and market sentiment, making it crucial to stay informed and ready to react.
- Effective strategies include trading based on seasonality, analyzing geopolitical news, understanding the natural gas/crude oil spread, and employing technical analysis.
- Regularly monitoring reports such as the Weekly Natural Gas Storage Report and the CFTC Natural Gas Report can provide valuable insights into market trends and potential price movements.
Here’s what you’ll learn on this page:
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Natural Gas Trading Basics
If you’re thinking about diving into the world of natural gas trading, you’re on the right track. But before you jump in, let’s break down the basics so you can start your trading journey with confidence.
To start, you can watch the video below:
Why Trade Natural Gas?
As the world increasingly shifts towards cleaner, more environmentally friendly energy, the demand for natural gas has surged. It’s considered a bridge fuel, not as clean as solar and wind power but much cleaner than coal and oil, making it a crucial part of the energy transition.
For natural gas traders, this commodity presents an exciting opportunity to bet on the future of energy. Whether you’re interested in long-term investments as the green economy grows or you’re looking to capitalize on short-term price movements, natural gas offers plenty of potential.
But that’s not all. Natural gas is also a major player in industrial usage. More and more companies are making the switch from oil to natural gas to power their operations, drawn by its cost-effectiveness and lower emissions. Even in the transportation industry, natural gas is gaining traction as a cheaper and cleaner alternative to petroleum and diesel.
All these factors combine to make natural gas a commodity with strong demand and robust trading opportunities. NG has enough volatility and liquidity to make it one of the most high-demand traded commodities in the world. As a result, many short-term traders focus on natural gas since they can easily get in and out of positions and make short-term trades.
What to Know Before Trading Natural Gas?
Before you start placing trades, it’s essential to understand some key aspects of the natural gas market. Here are the basics you need to know:
1. Trading Units: Natural gas is typically traded in units of million British thermal units (MMBtu). This is the standard measure of energy content and is crucial for pricing and trading contracts.
2. Natural Gas Trading Hours: Natural gas is traded almost around the clock, but it’s important to know the specific hours for your platform. On the NYMEX, natural gas futures trade from 6:00 PM to 5:00 PM ET, Sunday through Friday. Platforms like CME Globex offer electronic trading 24 hours a day, six days a week, with a short break each day. Make sure you’re aware of these schedules so you can plan your trades accordingly.
3. Volatility: Natural gas prices are known for their volatility—often more so than many other commodities or currency pairs. This volatility can create both opportunities and risks, so it’s crucial to be prepared for significant price swings.
4. Spreads: The spread, or the difference between the bid and ask price, can be relatively wide in natural gas trading. This can lead to higher trading costs, so it’s important to factor this in when planning your trades.
5. Leverage and Margin: Trading natural gas, especially through CFDs, involves leverage, which can amplify your gains—but also your losses. Understanding margin requirements and employing solid risk management strategies is vital to protecting your capital.
How to Trade Natural Gas?
Just like any other commodity, natural gas can be traded in several ways, each offering its own set of opportunities and risks. Let’s dive into the most common methods: Contracts for Difference (CFDs), futures, stocks, and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs).
1. Contracts for Difference (CFDs)
CFDs are a popular choice for traders who want to speculate on the price movements of natural gas without actually owning the asset. With CFDs, you can trade on margin, meaning you only need to put down a fraction of the total trade value to open a position. This leverage can amplify your profits, but it also increases your risk.
The beauty of natural gas CFDs lies in their flexibility—you can profit from both rising and falling markets. However, keep in mind that CFDs are generally more suited for short-term trading like day trading or scalp trading, and it’s crucial to have a solid risk management strategy in place.
2. Futures
Trading Natural Gas Futures contracts is another avenue to consider when trading natural gas. These contracts obligate you to buy or sell natural gas at a predetermined price on a specific date in the future.
The natural gas futures contract is traded on exchanges like the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX), and it is often used by both speculators and companies looking to hedge against price fluctuations.
Trading futures requires a good grasp of the market because the prices can be highly volatile. It’s not uncommon to see significant price swings based on supply and demand changes, weather patterns, or geopolitical events. It is, therefore, highly recommended to learn how futures trading works by reading one of the top futures trading books.
3. Stocks & ETFs
If you’re more interested in the broader energy market or prefer a less hands-on approach, trading stocks or ETFs could be the way to go. Investing in stocks of companies involved in the natural gas industry—like producers, distributors, or even equipment manufacturers—allows you to gain exposure to the market without directly trading the commodity.
On the other hand, ETFs offer a more diversified approach, as they often include a basket of natural gas-related assets. ETFs can be a great option if you’re looking for a long-term position investment strategy with potentially lower volatility compared to trading futures or CFDs.
As a natural gas trader, staying updated on the supply and demand factors and geopolitical developments involving these key players is crucial. It’s not just about watching the charts; it’s about understanding the bigger picture that drives those price movements.
Best Natural Gas Trading Strategies
Having a well-rounded strategy is key to trading natural gas. Natural gas markets can be highly volatile, driven by a mix of seasonal patterns, geopolitical events, and technical signals.
Let’s explore some of the most effective strategies you can use to trade natural gas:
1. Natural Gas Seasonality and Weather
One of the most significant factors influencing the price of natural gas is seasonality, particularly weather patterns. Natural gas demand typically peaks during the winter months when heating needs increase, leading to higher prices. Conversely, during milder seasons like spring and fall, demand tends to drop, which can lead to lower prices.
As a trader, understanding these seasonal trends can give you an edge. For example, you might consider taking a long position leading up to the winter months or a short position as warmer weather approaches.
Weather forecasts can also play a crucial role in short-term trading strategies. Sudden changes in weather predictions, such as an unexpected cold front, can cause sharp price movements.
Staying informed about these developments and reacting quickly can be the difference between a successful trade and a missed opportunity.
2. Trading the News: Fundamental Analysis
Natural gas markets are highly sensitive to geopolitical events and economic news. Major developments like conflicts in gas-producing regions (such as the Middle East or Russia), changes in government energy policies, or shifts in global supply chains can all have a significant impact on natural gas prices.
For instance, the recent tensions between Russia and Europe over gas supplies can cause prices to spike due to fears of supply disruptions.
Therefore, keeping a close eye on the news and understanding how these events might influence market sentiment is crucial. You can use this information to anticipate price movements and make informed trading decisions. Whether you’re trading futures, CFDs, or other instruments, integrating fundamental analysis into your trading strategy can help you navigate the complexities of the natural gas market.
For more information about natural gas prices and recent updates and news, you can visit our daily natural gas market analysis page.
3. Trading the Natural Gas/Crude Oil Spread
Known as the commodity spread trading strategy, the natural gas/crude oil spread is popular among traders who want to capitalize on the price relationship between these two energy commodities. While both natural gas and crude oil are energy sources, their prices don’t always move in tandem, which can provide lots of trade opportunities (as presented in the chart below).
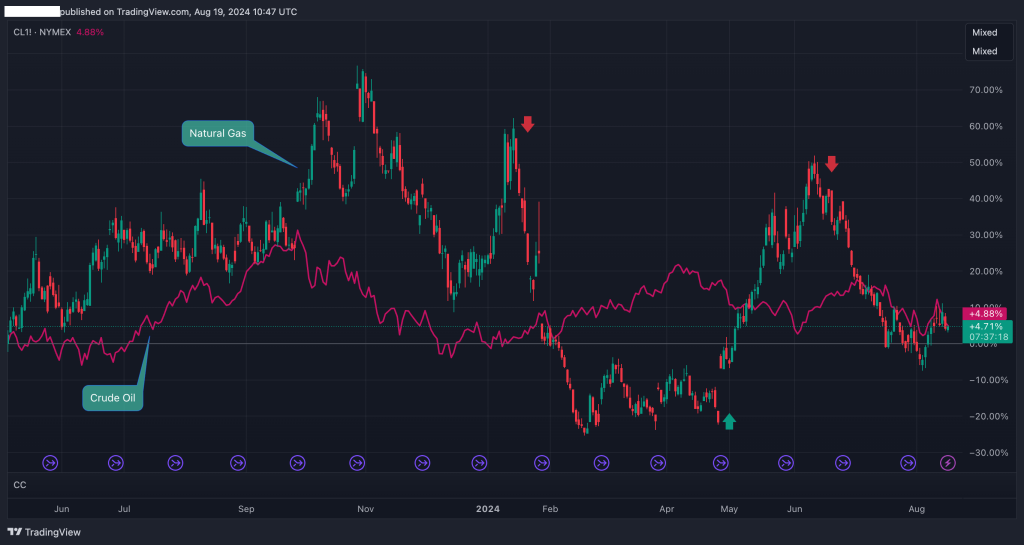
Factors such as differing supply dynamics, seasonal demand, and geopolitical events can cause the spread between these two commodities to widen or narrow.
To trade the spread, you would typically go long on one commodity while shorting the other based on your analysis of their price relationship.
For example, if you believe that natural gas is undervalued relative to crude oil, you might go long on natural gas and short on crude oil. This strategy can help you profit from relative price movements while potentially reducing your overall risk.
4. Natural Gas Technical Analysis
Last but not least, let’s talk about technical analysis. Even if you’re all about the fundamentals, technical analysis is your go-to tool for finding precise entry and exit points. It’s like having a map that helps you navigate the twists and turns of the market.
Start with something simple, like moving averages. The 200-day moving average is a solid indicator of the overall trend. If natural gas prices are above this line, you’re likely in a bullish trend; if they’re below, it’s probably bearish territory. Combine this with other tools like Fibonacci retracements, and you’ll have a clearer picture of where prices might turn.
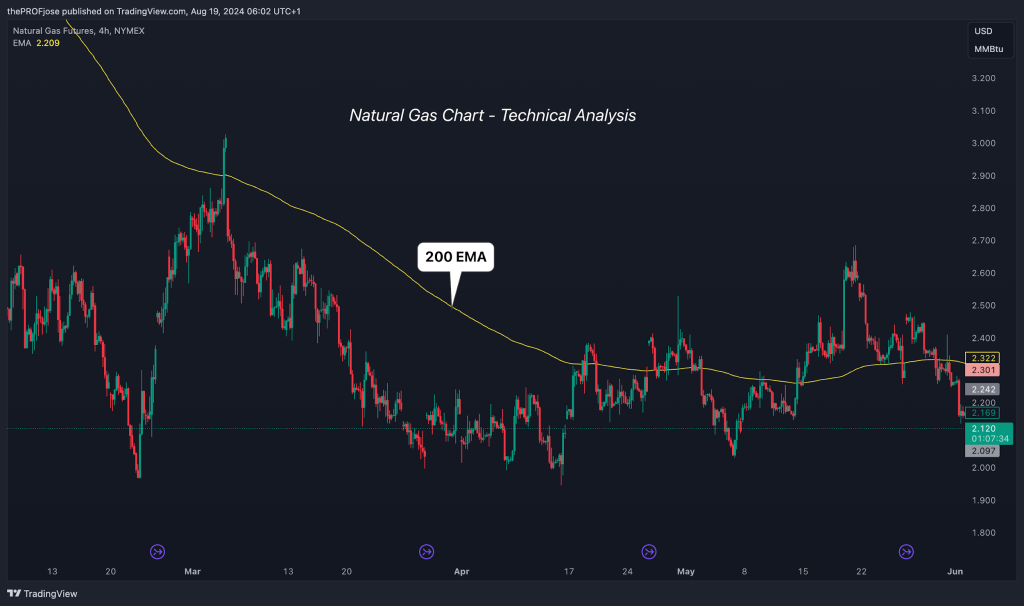
For example, as you can see in the chart above, if natural gas prices pull back to a key Fibonacci level during an uptrend, that could be your cue to buy. It’s all about using these tools to stack the odds in your favor.
You can also explore other trading strategies like the breakout trading strategy, supply and demand trading strategy, and many more.
What to Look for When Trading Natural Gas?
When it comes to trading natural gas, there are a few key factors that can make or break your strategy. The natural gas market is influenced by a complex web of elements, ranging from supply-side dynamics to macroeconomic indicators. Understanding these factors can help you make more informed trading decisions.
Let’s break down what you need to keep an eye on.
Supply-Side Developments
First and foremost, let’s talk about the supply side of the equation. Natural gas production is dominated by a few key players, and their production levels can significantly impact prices.
The United States, Russia, and Qatar are among the largest natural gas producers globally, and any changes in their production levels can cause ripple effects throughout the market.
For instance, if the U.S. ramps up its natural gas production, it could lead to an oversupply in the market, pushing prices down. On the other hand, if geopolitical tensions disrupt production in Russia or the Middle East, supply could tighten, leading to higher natural gas prices.
As a trader, staying updated on the supply and demand factors and geopolitical developments involving these key players is crucial. It’s not just about watching the charts; it’s about understanding the bigger picture that drives those price movements.
Natural Gas Reports
To get a real-time pulse on the natural gas market, you’ll want to pay close attention to various reports that are released regularly on the economic calendar.
The Weekly Natural Gas Storage Report from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a must-watch. This report gives you a snapshot of the current supply levels and can provide clues about future price direction. A higher-than-expected storage level might indicate oversupply, which could lead to lower prices, while a lower-than-expected level might suggest rising demand and potential price increases.
Then there’s the CFTC Natural Gas Report, which provides insights into the positions of major players in the futures market. Are hedge funds heavily shorting natural gas? Are commercial hedgers increasing their long positions? These insights can help you gauge market sentiment and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Lastly, the Gas Quarterly Report offers a broader view, including projections and trends that could affect natural gas prices over the longer term. Keeping these reports on your radar will equip you with the data you need to anticipate market shifts.
Inflation Data
Now, let’s talk about the macroeconomic side of things—specifically, inflation. Inflation can have a significant impact on natural gas prices, primarily through its effect on demand.
When inflation is high, the cost of goods and services rises, which can lead to reduced consumption across the board, including energy. High inflation often results in higher interest rates as central banks attempt to control it, which can further dampen demand for natural gas, particularly in industrial sectors.
On the flip side, during periods of low inflation or deflation, the purchasing power of consumers and businesses increases, which can boost demand for energy, including natural gas. Understanding how inflation trends evolve can give you a better sense of where natural gas prices might be headed.
Conclusion
In sum, trading natural gas is about understanding the market’s unique patterns and using that knowledge to spot opportunities. From seasonal demand changes to geopolitical events, the natural gas market offers plenty of potential for those who are prepared. And the good thing, natural gas is an exciting market in terms of trading it, and understanding what drives the commodity’s price movements.
With the strategies and insights we’ve discussed, you’re ready to approach this market with confidence. So, as you step into the natural gas market, keep these strategies in mind and start making informed decisions that can lead to real results.
Risk Disclosure: The information provided in this article is not intended to give financial advice, recommend investments, guarantee profits, or shield you from losses. Our content is only for informational purposes and to help you understand the risks and complexity of these markets by providing objective analysis. Before trading, carefully consider your experience, financial goals, and risk tolerance. Trading involves significant potential for financial loss and isn't suitable for everyone.