Trading is all about getting information and knowing how to interpret this data to find successful trades. If so, then you can assume that the most crucial factor for success in trading is the reliability and the format in which a trader receives the information.
- Level 2 trading provides a comprehensive insight into the market’s order book.
- Level 2 quotes offer an in-depth view into the market, beyond just the last bid and ask prices.
- Understanding the difference between Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 data is crucial for informed trading decisions.
- Accessing and interpreting Level 2 market data can elevate your trading strategy.
Level 2 quotes are by far the ultimate market data source to get more detailed and complete information.
So, in this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about trading using the level 2 order book. We’ll also help you find ways to access level 2 data and explain the difference between level 1 and level 2 and level 2 and level 3.
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- What is Level 2 Data?
- What are the Components of A Level 2 Market Data?
- How Do You Read Level 2 Data for Day Trading?
- The Benefits of Using Level 2 Trading Data
- What are the Limitations of Level 2 Trading Data?
- Level 2 Trading Data for Different Financial Markets
- Tips on How to Trade with Level 2 Data Profitably
- Level 2 Trading PDF Free Download
- Can I Find a Level 2 Trading Demo Account?
- What is the Difference Between Level 2 and Level 3 Trading?
- Can You Trade CFDs with Level 2 Data?
- Bottom Line
What is Level 2 Data?
Level 2 market data is an order book that gives retail traders and institutional players a more detailed set of information about the traded asset. Unlike the level 1 order book that shows the last bid prices and ask prices, level 2 shows the complete list of bid and ask the market maker who placed the order, and the quantities (the size of the order).
In most cases, level 2 order boxes show around 5-10 best bid and ask prices, though, in some exchanges, you may get access to up to 40 bid and ask prices. To be able to use level 2 market data, a trader must have access to assets traded on an exchange. So, for example, when trading assets on a stock exchange, options, or futures contracts (commodities, forex, indices, etc.) – a trader can get access to level 2 data.
Trading with level 2 data is a necessary trading tool for active intraday traders and scalpers. Almost every proprietary trader uses a level 2 order book to analyze the markets and place orders. Many of these traders will tell you that it’s impossible to day trade without using the level 2 data service.
Below, you can check this bite-size video on the power Level 2 Trading with Level 2 Market data.
What are the Components of A Level 2 Market Data?
When you open any level 2 market data, regardless of the exchange it’s from, three major components are often present. They are the name or market maker placing the trade, the bid / ask price, and the trade size.
1. The Market Participants
The column on the left is one of the first few things you’ll notice on the level 2 data. This column is reserved for the market maker through which the trade was placed. Depending on what exchange’s Level 2 data you use, you may see this as MM or MPID (Market Participant ID).
So, if you see the name of a market maker, it means they (or another trader through them) have placed an order.
Here an exhaustive list of MPIDs, including their names, location, and telephone:
NasdaqTrader MPID List
2. Bid /Ask Prices
These are the prices at which the buying and selling take place. You’ll often find separate sections for the bid and ask prices, with the bid orders on the left and the ask orders on the right. The bid prices are those price levels where orders to buy are, while the ask prices are where orders to sell are.
3. The Size
You’ll also see the size of every trade that’s being carried out. In the stock market level 2 data, this size refers to the number of shares that are being traded.
How Do You Read Level 2 Data for Day Trading?
Level 2 is often perceived as a complex data service; however, knowing how to read and understand level 2 trading is actually very straightforward.
Simply put, a level 2 market depth order book shows the asset’s supply and demand offer in real time. In addition, the vast majority of level 2 order books on different trading platforms look pretty much the same, so once you learn how to read and analyze level 2 data, you’ll be able to use it on any trading program.
As you can see in the image below, the list of buyers is on the left side of the screen, and the list of sellers is on the right side. In this example, the first buyer offers to buy 600 shares of Intel at the stock’s price level of 29.33 via the INCA market maker (Instinet). On the right side of the screen, the first seller is willing to sell 1000 shares at 29.36 via the NFSC market maker. This is, in a nutshell, how level 2 market data works on the NASDAQ stock exchange.
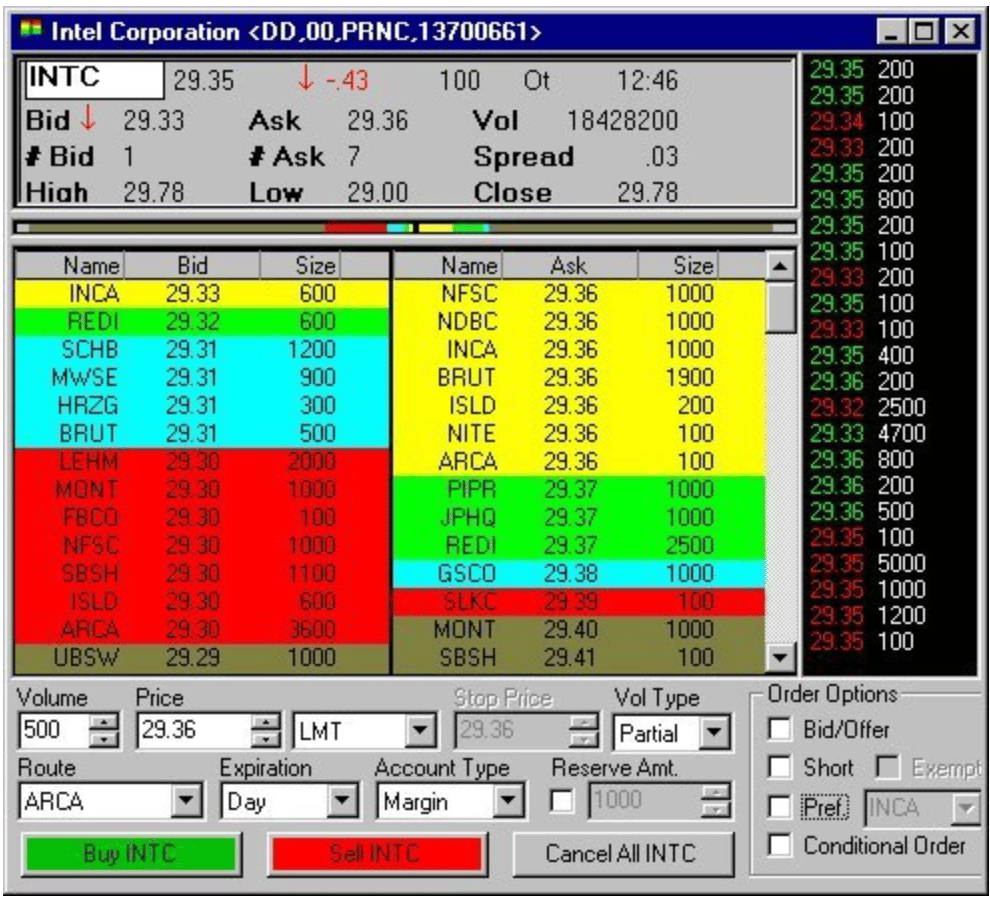
Moreover, the level 2 order book also shows a time sales box where you can see every transaction made on the specific market, including the price and quantity. If the transaction is displayed in red, it means that the order was made on the bid side. If the transaction is displayed in green, it then means that the order was made on the ask side.
Note that the time and sales screen is an extremely valuable asset for day trading. Because the market is highly manipulated by market makers who place orders and suddenly disappear or use various automated order types – the time and sales will help you get facts and see only the executed trades.
What are the Benefits of Using Level 2 Trading Data?
Trading with level 2 data is a necessary trading tool for active intraday traders and scalpers. Almost every proprietary trader who consults a level 2 order book uses it to analyze the markets and place orders. Many of these traders will tell you that it’s impossible to day trade without using the level 2 data service.
Some of the key benefits of using level 2 trading data include:
1. More Information
The main benefit of using a level 2 order book is, obviously, the wealth of data and information related to the specific asset. While level 1 gives you the first buyer and seller, level 2 gives you much more information.
Additionally, level 1 could be highly misleading as many traders use a unique technique known as AX trading. By using this technique, a trader is placing 100 shares to sell, but the order book shows just one share (yes, it’s possible to do that). In the level 1 order book, you would think that selling pressure is rising (as you’ll see one share on the bid side), while in the level 2 order, you can see how buyers are eager to buy more as you can see the full list of buyers and you can identify this trick.
In some scenarios, you can also know when a big institution enters a specific market. In commodity futures and bond futures markets, you can even identify when governments are entering and buying (or selling) in large amounts. In forex trading, this phenomenon is known as order blocks forex.
Furthermore, once you learn how to identify when a big player is entering the market, you can take a direction with the institution or big investors that have a significant position in the market or the other way. With level 2 data, there are many tricks and new ways to predict where the market might go next.
2. Easier to Know the Market Sentiment with Level 2 Market Data
Undoubtedly, as you have more information about the specific asset, you may better understand and feel the sentiment in the market. Just visualize it like a food market where buyers and sellers battle to get the best prices for their interests.
Well, that’s level 2 market data – the ultimate tool for centralized exchanges to present a real sense of a market. For that reason, many traders who utilize the naked trading strategy usually use level 2 market data to analyze the markets.
3. You Get the Best Prices
Another benefit of using level 2 data quotes is that you can negotiate to get the best available market prices. In other words, you can change your orders, set subsequent orders, etc.
This is particularly important when you trade derivatives and options. For example, let’s assume you are trading the Apple stock 146 June call option contract with a level 2 market data, and the Apple share price (underlying asset) is trading at 146.14.
The orders placed in the market are based on the price movement of the AAPL share price, and thus, every price movement impacts the option price. In this case, let’s say the Apple stock price action is rising, and you placed an order to sell the option at 2.48 when the bid price is 2.41. Then, as soon as you noticed the price is rising, you can immediately change your order to 2.50, 2.55, or even higher to get the highest price.
To sum up, here’s a comparison table of all the different types of market data – level 1, level 2, and level 3.
| Market Data Level | Data |
| Level 1 | Best bid and ask price + quantity on each side |
| Level 2 | Market depth of typically up to the 5-10 best bid and offer prices + quantity + market maker |
| Level 3 | Market depth is typically up to the 5-10 best bid and offer prices + quantity + market maker |
What are the Limitations of Level 2 Trading Data?
Level 2 market data may have many strong benefits, but they aren’t without their limitations. Here are some of these:
1. Not Suitable for Long-Term Investors
How far you can analyze the potential price of the security is heavily dependent on how much data the exchange shows you. And most exchanges only go as far as 40 rows of level 2 data at any point. As a result, traders who are looking to place longer swing trades and even positional trades won’t have enough data to analyze. That is why level 2 is only great for scalpers, day traders, arbitrage traders, and high-frequency traders.
2. You’re likely to be the first victim of manipulative market makers
That you can see the positions of market makers doesn’t mean you can also “trade with the smart money.” In fact, some market makers try to manipulate the market by placing orders, knowing that level 2 retail traders will see these orders and likely mimic their trades. The market makers then suddenly delete their orders or take the opposite side of the trades, leaving you hanging or in a loss. The idea is this. Don’t trust the orders on level 2 data completely. They could be manipulative.
3. Inaccessible for Some Markets
Stock market traders will enjoy using level 2 data because it’s relatively easy to access. Forex and CFD traders, however, will have a hard time accessing level 2 trading data.
Why? Stock is traded through regulated and transparent central exchanges such as Nasdaq and NYSE. Forex and CFDs are traded over the counter (OTC). It’s hard to track orders from this end. Your forex broker, for instance, is usually not the market maker. The broker has to parse your order through market makers, and in some cases, multiple market makers. Also, your broker may not be the only one using that market maker.
So, the complexity of tracking level 2 data for non-exchange-traded markets continues to pile. As a result, some brokers find it unprofitable and unnecessary to provide level 2 data for these markets.
4. Level 2 data can be confusing to read for volatile markets
Volatile markets are hard to read because you really can’t tell which is a “small order” or a “big order.” A security can trade at low volumes one day, and on the next, you will see things spiking and prices rising to mammoth levels.
Level 2 Trading Data for Different Financial Markets
Generally, you can trade almost any asset using level 2 market data. As long as the asset is listed on an exchange, you’ll be able to get access to level 2 trading. However, the benefits of using level 2 market data have a higher impact on some markets than others.
Level 2 Option Trading
Level 2 options trading offers more flexibility in terms of how traders can trade options. In my view, if you are planning to trade options, the first thing you should do is to get access to level 2 options data. Even if you do not use level 2 as a trading strategy, it’s a must-have tool for trading options.
The main reason is that options are derivative instruments tied to the underlying asset. So, the option’s price often stays the same for several minutes or even hours. However, the orders in the level 2 order book change constantly, and in many cases, you can use it to your advantage.
Level 2 Data in the Stock Market
As stocks and ETFs are traded on centralized exchanges, this is the easiest way to access level 2 trading. As a matter of fact, most banks and online brokerage firms offer level 2 stock trading as part of their basic packages. Furthermore, with a quick search, it is even possible to get stocks and ETFs level 2 data for free online.
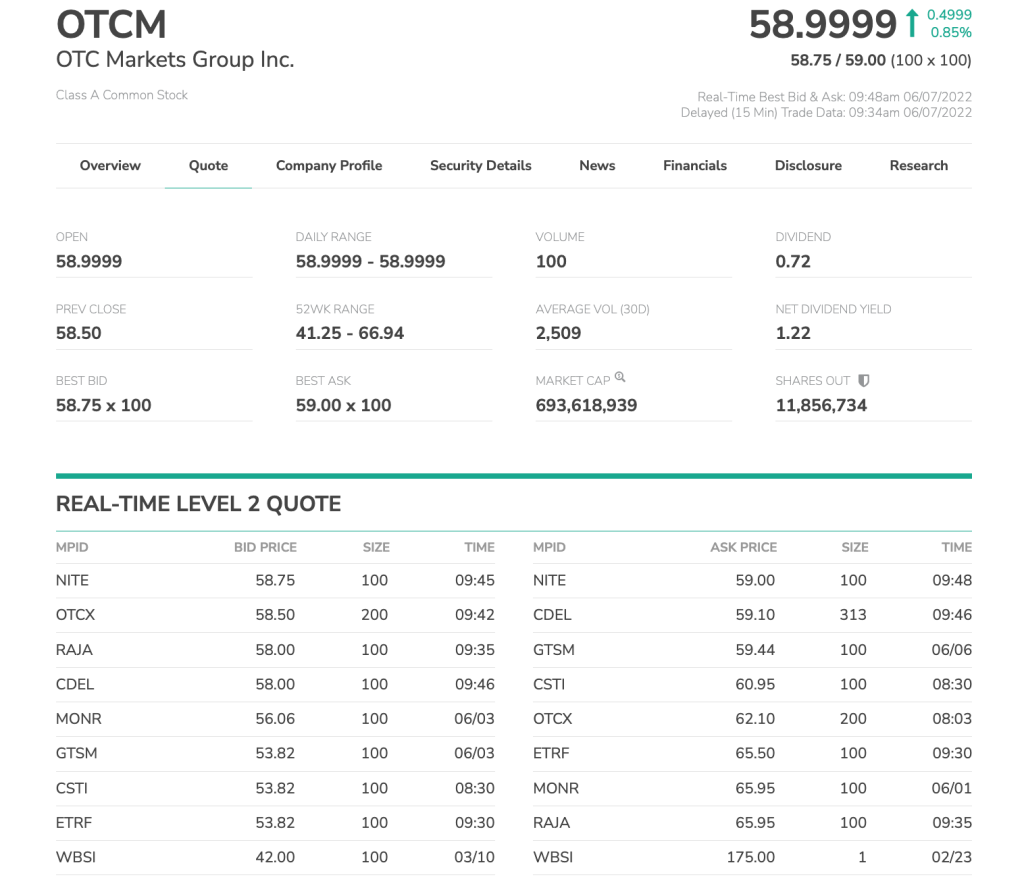
Day trading stocks, ETFs, and especially penny stocks using level 2 data is highly recommended. Most active Penny stocks trade on the OTC and have a low trading volume, meaning it is fairly easy to manipulate prices. For that matter, level 2 can be incredibly useful. For instance, when you notice an important market maker placing a large bid and the order flow is changing – it would potentially be a successful trade.
Here’s an example of what level 2 data looks like on a web page. Source: OTCMarkets.com
Level 2 Data Futures Trading
The futures market is the most important and developed financial market worldwide. This is where commodities, metals, global indices, interest rates, bonds, and FX currency pairs are traded and shipped worldwide. So, being the most developed market, it is not surprising that you get access to level 2 data, meaning you can trade any asset listed on the specified exchange with level 2.
However, take into consideration that this service is usually costly. Assuming you’d like to open a futures trading account and get access to level 2 data, you need to focus on one market. Otherwise, it could be expensive as brokerage firms charge a high fee for providing level 2 data.
Level 2 Data in the Forex Market
Getting access to level 2 data in the forex market is perhaps the most complicated of all. The reason is that the forex market is decentralized, where there’s no exchange or physical location where traders buy and sell currency pairs.
Yet, if you wish to trade currency pairs with level 2 data, you can do it in the following ways: trade FX currency pairs via future contracts or open an account with an Electronic Communication Network (ECN/STP) or Direct Market Access (DMA) forex broker. The first option requires a high initial deposit and typically high fees. The second option requires a lower initial deposit, though you must check with the brokerage firm to ensure they offer access to level 2 data.
Tips on How to Trade with Level 2 Data Profitably
As we have previously mentioned, the level 2 order book is a valuable and effective trading tool. So, you need to get familiar with several techniques and trading strategies when using level 2 market data. Those include:
1. Low Liquidity Can Be an Advantage
A common technique among day traders is to find markets with low liquidity and set orders on both sides or get an execution on one side and switch to the other. It’s a risky strategy, but it may generate consistent profit over the long run if you learn how to master this technique.
By being completely neutral when using this trading strategy, you basically wait in the queue on the bid or ask side. Then, once the order is executed, you can place another order on the other side and wait again in the queue.
2. Scalp Trading
Scalpers typically try to capture minimal price movements – a few ticks, cents, etc. They use one-minute or five-minute charts and often make many daily transactions to collect small profits.
To scalp trade, they must use level 2 trading data and various automated order types. As they usually buy and sell large numbers of shares, futures contracts, or forex lots – they use sophisticated market orders to open and close their traders without showing the number of shares they hold.
3. Trading Breakouts
Even though it is possible to trade breakouts with a level 1 order book, doing it with a level 2 data book is much clearer and more effective.
When you look at the price ladder with level 2 data, and you see the pressure building up or down to break the highest or lowest level of the day (or week/month, etc.), then you can easily find the right entry-level and make profits while trading the breakout. Ultimately, you can build a trading strategy entirely around this concept.
4. Follow the Prints
As we mentioned earlier, the time and sales screen is a vital tool for understanding the flow in the chosen market. If you know how to read it correctly and avoid all the false order placements made by market makers, you can find many trade entry and exit points. That is why order flow analysis is one of the best methods for using level 2 data for day trading.
For example, if you notice print after print of sell orders on the bid side, that means sellers are willing to sell the asset at any given price on the bid side. There’s no doubt that the momentum is bearish in such a scenario, and you’ll enter a short-selling position (or exit an existing long position).
Level 2 Trading PDF Free Download
If you need something to easily carry around and refer to when it comes to level 2 trading, this PDF is for you:
How Do You Find a Level 2 Trading Platform?
Well, it’s not so easy, and some brokers charge a high fee for access to level 2 data. But first, to find a level 2 trading platform, you must find a brokerage firm that gives you direct access to a centralized exchange. Additionally, it’s better to focus on one market to reduce the cost of the trading platform.
That said, some of the most popular (and low-cost) brokerage firms offering level 2 market data include TD Ameritrade, InteractiveBrokers, FirstTrade, Robinhood, Fidelity, TradeStation, NinjaTrader, etc. Additionally, many online banks offer to trade with level 2 data.
Can I Find a Level 2 Trading Demo Account?
Only a few brokerage firms offer a free demo account with access to level 2 trading. Still, from our research, some of the best online brokers offering level 2 data on a demonstration account include Sterling Pro, TD Ameritrade ThinkorSwim, and IG Markets.
What is the Difference Between Level 2 and Level 3 Trading?
Brokerage firms offer two types of DOM (depth of market) – level 2, also known as L2, and level 3, known as L3. There’s not much difference between the two except that level 3 shows a long list of buyers and sellers than what a trader will get using level 2. The most significant benefit of using level 3 is predicting and placing stop orders and taking profit orders.
Can You Trade CFDs with Level 2 Data?
Theoretically, it’s possible, but you cannot really trade CFDs with level 2. Some CFD brokerage firms give you access to level 2 data, although the CFD contract has level 1 data only. You can use the level 2 data to make trading decisions and analyze the market; however, you cannot place orders and see them in the order book. This is because CFDs are derivative contracts traded outside exchanges and usually involve just two parties (a trader versus the broker or other traders in the network).
The Bottom Line
Most day traders incorporate level 2 market data into their trading setup as it gives them a clearer picture of what’s happening in the market. It is one of the most valuable tools as it provides more detailed real-time data for a given asset and ultimately can lead to various strategies and techniques to trade the markets.
If you plan to do a day or scalp trade, level 2 market data can open a new door for you to the trading world. Of course, it does not guarantee success, but it will help you develop new ways to see the markets, understand how prices move, and how market makers can push prices in a specific direction.
Risk Disclosure: The information provided in this article is not intended to give financial advice, recommend investments, guarantee profits, or shield you from losses. Our content is only for informational purposes and to help you understand the risks and complexity of these markets by providing objective analysis. Before trading, carefully consider your experience, financial goals, and risk tolerance. Trading involves significant potential for financial loss and isn't suitable for everyone.





