A Book Brokers vs B Book Brokers
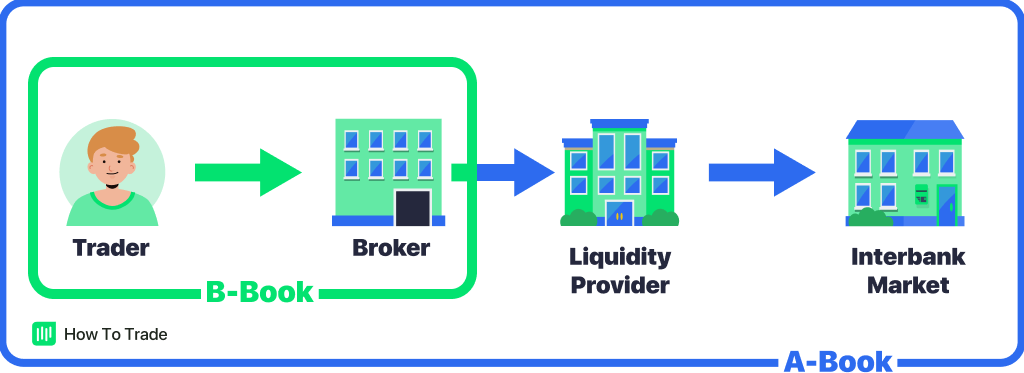
No matter what market you trade, you can only access the financial markets through a broker. They connect forex retail market participants with to liquidity providers.
For that purpose, there are two types of brokers: A Book broker and B Book broker. Most brokers use a mix of both models, but it’s essential to know how each works and what that means for you as a trader.
Let’s get to it.

What are A-Book Brokers?
An A-Book broker operates on what’s called a ‘no dealing desk‘ model. This means that when you place an order to trade a currency pair, say GBP/USD, the broker sends your order to a liquidity provider, like a bank. This liquidity provider matches your trade with an opposite side trade.
The A-Book process is synonymous with a traditional brokerage role. A facilitator of transactions, sort of. They offer you a direct and reliable connection to the global forex market through STP (Straight Through Processing) or ECN (Electronic Communication Network) accounts.
ECN accounts route your orders directly to the interbank market, where the orders get filled. An STP account, on the other hand, often has more than one liquidity provider. These liquidity providers can be other the interbank market, STP brokers, or even ECN brokers.
How do A-Book Brokers Process Trades?
- You decide to buy GBP/USD and place your order with an A-Book broker.
- The broker forwards your order to a liquidity provider, who finds another market participant wanting to sell the same pair.
- Your order is matched, and the trade is executed.
Usually, the A Book broker does this with fairly competitive bid-ask spreads.
Advantages of A-Book Brokers for the Retail Trader
These are some of the advantages of A-Book Brokers:
- Transparency: Orders are passed to the interbank market, providing clarity over execution.
- No Conflict of Interest: Brokers profit from trade volume, not from trading losses, aligning their interests with the traders’.
- Market Execution: Orders are filled at the best possible market rates, ensuring fair pricing.
Disadvantages of A-Book Brokers for the Retail Trader
Here are some of the disadvantages of the A-Book Model:
- Variable Spreads: Can widen significantly during major news events or low liquidity, increasing trading costs unexpectedly.
- Commission Fees: Retail traders may have to pay a commission on top of spreads, increasing the cost per trade.
- Slippage: The best price may not be available, and orders may be filled at a slightly different price than expected.
How Does the A-Book Forex Broker Make Profit?
A-Book forex brokers make their profits via a small mark up on the spread/commission that you directly pay when placing trading orders. Assume the spread from the liquidity provider is 3 pips, your A Book broker may list it on their platform as 4 pips, guaranteeing them a 1 pip profit. Therefore, the more you trade, the more they will make.
They obviously want your trading account to be active – they don’t care if you are winning or losing; all they want is that your trading volume will be as high.
Think of a real estate broker or a stockbroker. They source the deal and, in return, earn a commission. It’s the same with A-Book brokers.
What Are B-Book Forex Brokers?
When placing a trade via a B-Book broker, they fill your trade in house. Forget the bank. You’re now buying directly from the supplier. So, a B-Book forex broker can be best described as a market maker who is responsible for always providing execution and paying the differences (losses or profits) to their clients.
How Do B-Book Brokers Process Trades?
Here’s what a B-Book execution looks like:
- You initiate a buy order for GBP/USD with a B-Book broker.
- The broker internally takes the opposite position, ‘betting against you.’
- The trade is executed within the broker’s system.
Some people will say that this execution model generates conflicts between the client and the broker. However, there are some advantages to trading via B-Book brokers. This includes very competitive spreads (sometimes as low as zero), fast execution, and the ability to get an execution on all instruments (including exotic currency pairs).
How Does the B-Book Broker Make Profit?
By betting against you.
Yes, really.
In the B-Book model, brokers make money when traders lose. They provide the prices, bear the market risks, and manage trades using their capital. That’s why they’re called market maker brokers or dealing desk brokers. They balance their books by hoping that losing trades will cover the winning trades they must pay out.
May sound crazy, but that’s how the inner workings of the brokerage industry operate.
What B-Book brokers have going for them is that they can offer better trade execution prices because they can immediately fill orders, which can be seen as beneficial to the trader.
Advantages of B-Book Brokers
Here are some advantages of B-Book Brokers:
- Fixed Spreads: Often offer fixed spreads, which can be advantageous during volatile market conditions.
- Lower Entry Requirements: B-Book brokers typically offer lower minimum deposit requirements, making it more accessible for new traders.
- Instant Execution: Trades are often executed instantly, reducing the waiting time for orders to be filled.
Disadvantages of B-Book Brokers for the Retail Trader
These are some of the drawbacks of using B-Book models:
- Conflict of Interest: Potential conflict exists since these brokers only profit when traders lose.
- Price Manipulation Risk: Theoretical risk of price manipulation, as the broker controls the execution and pricing.
- Profitability Limitations: Extremely profitable traders might be “penalized” as they can be viewed as a risk to the broker’s profitability.
How Does This Affect You?
As a trader, it’s not about labeling one model as good and the other as bad, but rather understanding which model aligns with your trading strategy. It’s about focusing on the price and execution quality you receive from your broker.
Some traders are uncomfortable with the idea of a broker benefiting from their losses, and it’s understandable. You know, the broker may start getting some unscrupulous ideas.
However, this is part of the Forex trading ecosystem, and both broker models can coexist with your strategy as long as you are informed and choose the broker that fits your trading needs the best.
Key Takeaways
- A-Book brokers route your trades directly to the interbank market or through liquidity providers.
- They offer variable spreads and are generally more trustworthy than B-Book traders because they’re not interested in seeing you lose money.
- The B-Book broker takes trades opposite to yours. When traders lose money, they win. And when traders make money, they lose money.
- They offer fixed spreads and fast execution because they are their own liquidity provider. The traders don’t go to interbank markets. Rather, they are executed by the broker who has taken the opposing sides of traders trades.
- Most brokers use a hybrid model where they be an A or B-book broker, depending on that their trader wants.
In partnership with our recommended partner
Wait!
"Join our Trade Together program and interact with us in real-time as we trade the markets together."
