Bid, Ask and Spread in Forex Trading
So far, we’ve described currency pairs as having just one price or exchange rate. But this is not entirely true. If you’ve ever used an online broker or a trading platform, you’ll notice that there are usually two sets of exchange rates or prices in front of a currency pair. Those two prices are called bid and ask prices, and the difference between them is called spread.
The rest of this lesson will shed more light on them, including how they influence your trading.
Understanding the Concept of Buying and Selling in Forex
Buying and selling in the foreign exchange market is not as straightforward as you may think. The number one reason for this complication is that in forex, we trade currency pairs, not single currencies.

The second source of complication is that in forex, we never really get to own any of the currencies in the pair we’re buying or selling.
For instance, when you buy GBPUSD, no one transfers Pound Sterling or Dollars to your bank account. You also don’t need to own either before entering a short position on the GBPUSD.
Because of these complications, it can be tricky to pinpoint what we’re selling or buying, what it means to buy or sell, and at what price we’re carrying out our transaction.
So, to help you understand what’s going on, you first need to know what an exchange rate is:
What are Exchange Rates in the Forex Market?
The exchange rate of a currency pair in forex is simply the amount of the quoted currency required to buy one unit of the base currency.
The example below shows the British Pound exchange rate versus the US dollar.

When buying, the exchange rate tells you how much you have to pay in units of the quoted currency to buy 1 unit of the base currency. In the example above, you must pay $1.27223 to buy £1. When selling, the exchange rate tells you how many units of the quoted currency you get for selling 1 unit of the base currency. In the example above, you will receive $1.27223 when you sell £1.
Exchange rates vary based on supply and demand, which is usually determined by interest rates and the central bank monetary policies of participating countries.
Next, what does it actually mean to buy?
What it Means to Buy in Forex
When you buy a currency pair in forex, you won’t own that currency pair. What you’re doing, though, is that you’re speculating that the exchange rate of that pair will rise, and you’re betting your money on it. If the price eventually rises, your broker pays you the difference between your buying price and the price when you opt out of the trade.
Let’s continue with our GBPUSD example from above. The exchange rate is 1.27223, and you buy. This means you speculate that the exchange rate of GBPUSD will increase. By clicking the “buy” button on your trading platform, you’re initiating a contract with your broker that allows you to profit or lose money from the price difference between the price you’ve bought at and a future price.
If the price rises to 1.27225 after a while, the difference would be three pips. So, if you traded on a standard lot size, you would gain $30 because a standard lot pip value in GBPUSD is $10. If the price falls instead by the same difference, you pay the broker that amount.
So, you see, you won’t own GBP or USD when you buy in forex. Instead, you’re speculating that the price will rise.
What it Means to Sell in Forex
You don’t need to own any of the currencies in a forex currency pair before you can sell it. Instead, you’re speculating that the currency pair’s exchange rate will fall, and you’re betting your money on it.
If the price falls to a lower price, your broker pays you the difference between your selling price and the price when you opt out of the trade.
Returning to our GBPUSD example. Clicking on the “sell” button means you think the price will fall. If it falls to 1.27220 from 1.27223, your broker calculates how much the difference of three pips translates to on your position size and pays it to you. But if the price rises to a higher price, you pay the difference.
Bid, Ask, and Spread in Forex Trading
Now that you understand what buying and selling truly mean in the forex market let’s delve into the bid and ask prices.
What is Bid Price?
The bid represents the price at which you can SELL a currency pair. It’s the one that comes first on the price quote on trading platforms.
Imagine you were trying to sell your old monitor to a shop that buys used ones. (Now that you’re a trader, you’ll need a new, bigger one!). To make a profit, the shop will need to buy your monitor at a price lower than the price they’ll sell it for.
If the store can sell the monitor for $600 and it most likely wants to make any money, the most it can buy from you is $599. In this situation, $599 is the bid price.
Let’s bring it back to Forex. In the quote GBP/USD 1.8812/1.8815, the bid price is 1.8812. This means you sell £1 for $1.8812. And when you execute your sell trade, this is your selling price.
What is Ask Price?
The ask is the market price in a trade at which you can BUY the currency pair from your broker.
Going back to our monitor imagination, imagine you didn’t have an old monitor to swap in the first place. You want to buy your first yet. The shop will sell it for you at a price higher than what they bought it for. If they bought it for $590, they would sell it for $600. This $600 is the asking price.
Returning to forex, in the quote EUR/USD 1.2812/1.2815, the ask price is 1.2815. This means you can buy €1 for $1.2815.
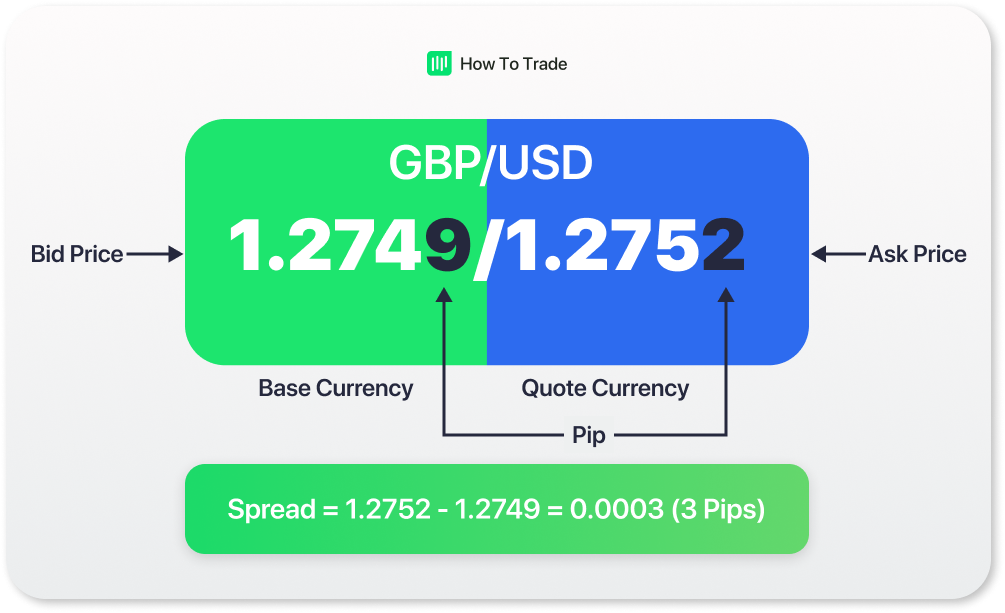
Typically, the ask rate will always be higher than the bid rate.
What is the Spread in the Retail Forex Market?
Spread is the difference between the bid and ask price. Some others call them bid-ask spreads. It is one of the ways a broker makes their money.
Generally, forex spreads are crucial in forex trading and selecting a good forex broker because they differ from one forex broker to another. When you enter a forex trade, you essentially start the trade with a loss because there’s a bid-ask spread between the two currencies. In most cases, this price difference is basically what you pay your broker, and only if the market moves in your direction (to cover the cost of spread) will you see a profit in your trade.
Let’s take the GBPUSD quote of 1.8812/1.8815 as our example again. The spread here is 3 pips, the difference between the bid price and the ask price. As soon as you initiate any foreign exchange transaction with your broker, your trade starts out at negative 3 pips (-3 pips).
Another factor to consider is that a forex spread varies depending on the instrument you are trading and its liquidity. Wide spreads are more common in foreign currencies that have low liquidity (minor and exotic currency pairs). And when a particular currency pair has a tight spread, it is a very volatile pair. Popular examples are EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and AUD/USD. For that reason, many forex traders choose to trade major currency pairs to avoid a wider spread and to be able to get in and out of positions quickly.
Types of Spread
Forex brokers offer two types of forex spreads:
- Variable Spread: Variable forex spreads fluctuate when market conditions change.
- Fixed Spread: Fixed spreads always stay constant, regardless of the market condition.
Most often, traders who trade frequently within a short period will find variable spreads more beneficial. On the other hand, long-term traders wouldn’t care so much about having their spread variable or fixed.
Key Takeaways
- An exchange rate is the amount of the quoted currency you would need to buy one unit of the base currency.
- You don’t actually have to own any of the currencies in a pair before you can buy or sell them in forex. You’re only speculating about their price movements, not buying and selling the actual currencies.
- We sell at the bid price, while the price we buy at is the ask price.
- The difference between the ask and bid prices is your spread. This spread is the primary method of earning for brokers.
A spread in the foreign exchange market is the primary transaction cost when you are involved in any forex trade. Therefore, it is not a surprise that you need to understand what they are, as they can significantly impact how you trade the markets.

