What is Margin in Forex?
As discussed in the previous lesson, when trading Forex, you only need to put down a small amount of capital, also known as the margin, to open a new position. This type of trading is known as margin trading and is one of the key reasons many traders are drawn explicitly to trading the forex market.
In this lesson, we’ll show you how margin works in forex and how to use leveraged trading in the forex markets effectively.
What is Margin in Forex Trading?
In simple terms, margin is a percentage of your funds that your brokerage firm sets aside to ensure that you can cover the potential loss of the trade. See it as collateral or a “good faith deposit.” Should you lose the trade, the broker takes it from you.
For example, if you want to buy $100,000 worth of USD/JPY, you don’t need to invest the full value. Instead, you only need to deposit a portion of the margin required by your forex broker (depending on your Forex broker and leverage). On a leverage of 1:20, for instance, your margin would be $5000.
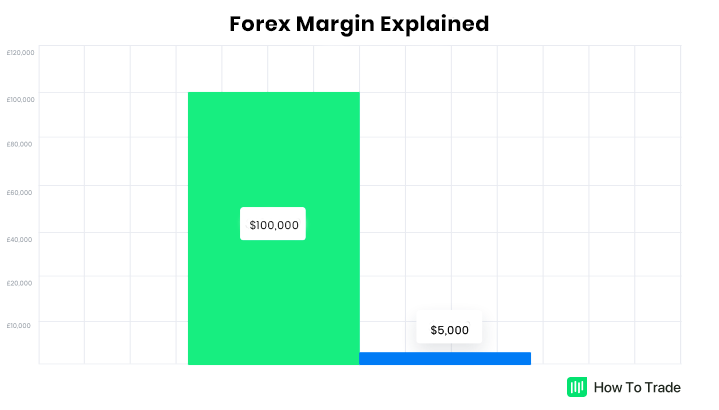
This portion is ‘locked up’ by your broker for the duration of the specific trade. Once the trade closes in a positive, the margin is released back into your trading account, and you can now use it again to open a new trade. This is, in a nutshell, how margin is used in the Foreign Exchange market.
Margin and leverage are inversely tied to each other. This means 2% margin translates to 1:50 maximum leverage. Also, 5% margin is 1:20 leverage.
Finally, Margin is not a transaction cost or a fee. It is simply the amount your broker keeps away from your entire account balance to keep your trade open.
What Is A Margin Requirement In Forex Trading?
Margin is usually expressed as a percentage of the full amount of the position. For example, most Forex brokers say they require 0.25%, 0.5%, 1%, 2%, 10%, or 25% margin. And when you trade forex, this percentage is known as the Margin Requirement.
Here are some examples of forex margin requirements for different currency pairs:
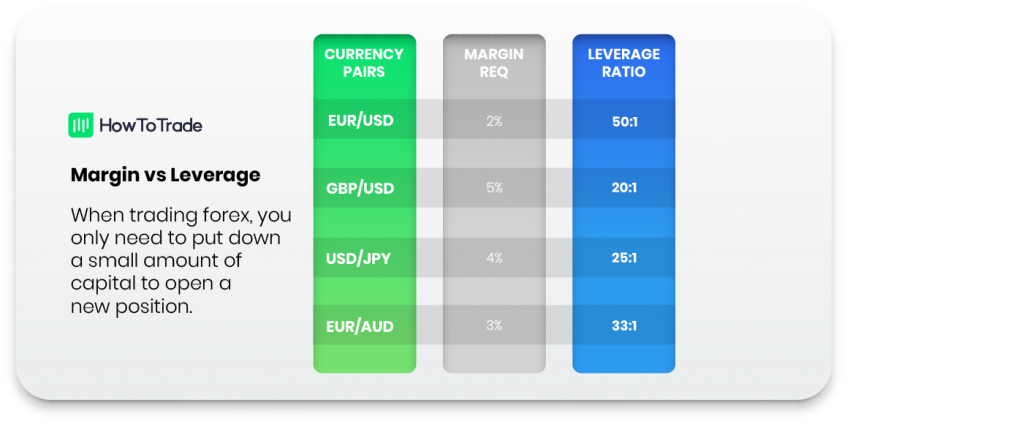
As you can see above, the forex margin requirement for the EUR/USD is just 2%, which means the broker provides a leverage ratio of 50:1. So, if you wanted to open a trade with a mini lot size, the nominal trade size is $10,000. But with a 2% margin, you only need to supply $200. It also means you can only have 50 open positions of that size at one time. This margin is called your initial margin.
For that matter, some forex brokers provide even a higher leverage ratio of up to 500:1 and even 1000:1. With that said, these ratios also significantly increase the risks involved in trading currency pairs and trading CFDs.
How To Calculate The Required Margin In Forex Trading?
If the base currency is the same as your account’s currency, this is the formula to calculate forex margin:
Required Margin = Notional Value x Margin Requirement
A perfect example is if you wanted to buy the USDJPY currency pair on a mini lot and you have $1000 in your forex trading account. This means you want to buy $10,000 worth of the position.
If your broker has a margin requirement of 5%, your required margin, according to that formula, would be $500.
However, if the base currency differs from your account’s currency:
Required Margin = Notional Value x Margin Requirement x Exchange Rate Between Base Currency and Account Currency.
For instance, assume you still have $1000 in your forex trading account, and you want to buy GBPUSD at 1.2700 on one micro lot. That means you’re buying 1000 units worth of position. On a margin requirement of 3%, your required margin, according to our formula, would be $38.1.
That means you only need $38.1 to open that trade.
You don’t have to calculate your margin manually. Your broker does that for you. You can also use a third-party forex margin calculator.
What is Free Margin in Forex Trading?
Forex free margin is the amount of margin left on your account that you can open new trades with. If you have a trade open, your free margin can rise or fall depending on the ongoing outcome of the trade. It’s gotten by subtracting your required margin from your account equity.
By the way, your account equity is the sum of your account balance and your unrealized profit or loss from your open positions.
Let’s take the USDJPY trade you had open from up there as an example. At the moment of opening the trade, this is what your forex account would be like.
Account Balance = $1000
Margin Required = $500 (5% of your $10,000 position)
Account Equity = $1000
Free Margin = $500 (The difference between account equity and margin in use)
But assume the position goes a few pips in your direction, and you’re in $100 profit. This is what your account would look like:
Account Balance = $1000
Margin Required = $500 (5% of your $10,000 position)
Account Equity = $1100
Free Margin = $600 (The difference between account equity and margin in use)
This means with your trade in profit, you can still open more forex trades using your $600 free margin even without first closing the currently opened trade.
The next thing you need to know is margin level.
What is Margin Level in Forex
Margin level is your forex broker’s way of telling you if you can still open trades based on what’s left in your account.
The formula for calculating your margin level in forex is given by:

When you have a margin level of 0% when you have no trades open. Typically, you want to keep your margin level as far away from 100% as possible. The farther away you are from 100%, the more trades you can open. Some brokers set their margin level limits at 100% so your trades are automatically closed when your margin level hits that level.
Let’s continue with our USDJPY example to illustrate your margin level. When you’re in $100 profit, your margin level, according to our formula, would be 220%. This is far enough away from 100%, so the account is very healthy. You can still open further trades.
But when the trade starts going against you, and your margin level falls to your broker’s limit, your open trades are closed. Before this happens, though, the broker notifies you that your margin is getting close to or below the margin level threshold. Such notifications are called a margin calls in forex trading.
- Margin is the minimum amount a forex trader must have to open a trade on their forex account. It’s the security deposit your broker takes to open a trade.
- The margin varies depending on the margin requirement of the broker and the position size you’re attempting to trade.
- Your account equity is the sum of your trading account balance and the profit or loss of your currently running trade(s)
- Free margin is the difference between hour account equity and the used margin.
- Margin level is the percentage of the ratio of your account equity to your free margin. The farther your margin level is from 100%, the more positions you can still open.
Conclusion
At this point, we believe you know everything you need to know before you begin trading on margin. Don’t forget that it is still possible to lose more than your initial deposit in a trade. To avoid this, you need to learn how to manage your trade like a pro.
In partnership with our recommended partner
Wait!
"Join our Trade Together program and interact with us in real-time as we trade the markets together."
