Macroeconomics in Forex Trading
The forex market is susceptible to many fundamental factors. This lesson explores how macroeconomics impacts the foreign exchange markets.
First, let’s show you the relationship between macroeconomics and the foreign exchange market.
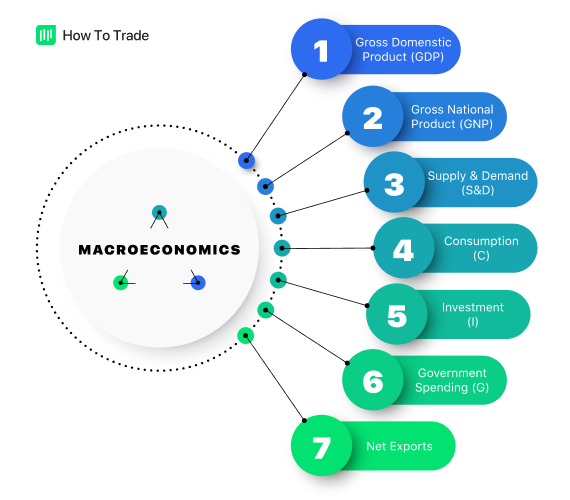
Macroeconomics in the Foreign Exchange Market
Macroeconomics is the study of how economies, markets, or industries function on a broad scale. As it pertains to conventional finance, macroeconomics quantifies a financial system’s performance. This is done via the scrutiny of three foundational elements: output, employment, and inflation.
Make no mistake — if you’re trading forex, then you’d best brush up on your Macroeconomics 101!
1. Economic Output
Economic output is the total value of all produced goods and services. One premier measure of output is the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which is typically viewed in relative terms on a quarterly or annual basis.
In foreign exchange trading, output is a key market fundamental. It is viewed from two perspectives: performance and growth. Performance is the current measure of output, while growth is the projected measure of future output.
An example of the performance/growth dichotomy may be observed by looking at Nominal and Real GDP. Nominal GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced during a specified period; Real GDP accounts for inflation by using constant pricing (more on inflation in a minute!).
As performance and growth indicators, nominal and real GDP are key elements of forex trading. Generally, when GDP values are positive, the exchange rate of the domestic currency appreciates. Conversely, the local currency lags versus other foreign currency values when GDP is negative.
2. Unemployment
For all economies, developed and emerging, unemployment levels are a vital macroeconomic indicator. Various metrics are used to measure unemployment. A few of the best-known among forex traders are the U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls report and the U.K. Unemployment Rate.
Generally speaking, employment levels and domestic exchange rates have a negative correlation. As a country’s unemployment grows, the domestic currency loses value. Why? There are two fundamental reasons:
- Economic Performance: During periods of high unemployment, output tends to suffer. As a result, the international currency markets are highly likely to discount the monies of regions with high unemployment.
- Monetary Policy: A common mantra among central bankers is “promoting maximum employment.” To do so, central banks adopt dovish policies to nurture employment and economic growth. Among these actions are the lowering of interest rates and the extension of credit. As a result, the domestic currency becomes devalued on the foreign exchange markets.
If you’re going to trade the forex market, don’t forget about unemployment! It is an excellent signal for understanding the macroeconomic state of a country, region, or the world as a whole.

3. Inflation
Inflation is a complex topic with various unique definitions. Perhaps the most common description is an upward movement in the pricing of an economy’s goods and services. When inflation rises, so do producer and consumer prices. It causes pricing instability and devalues the domestic currency. So, when an economy experiences inflation, the local currency loses its value.
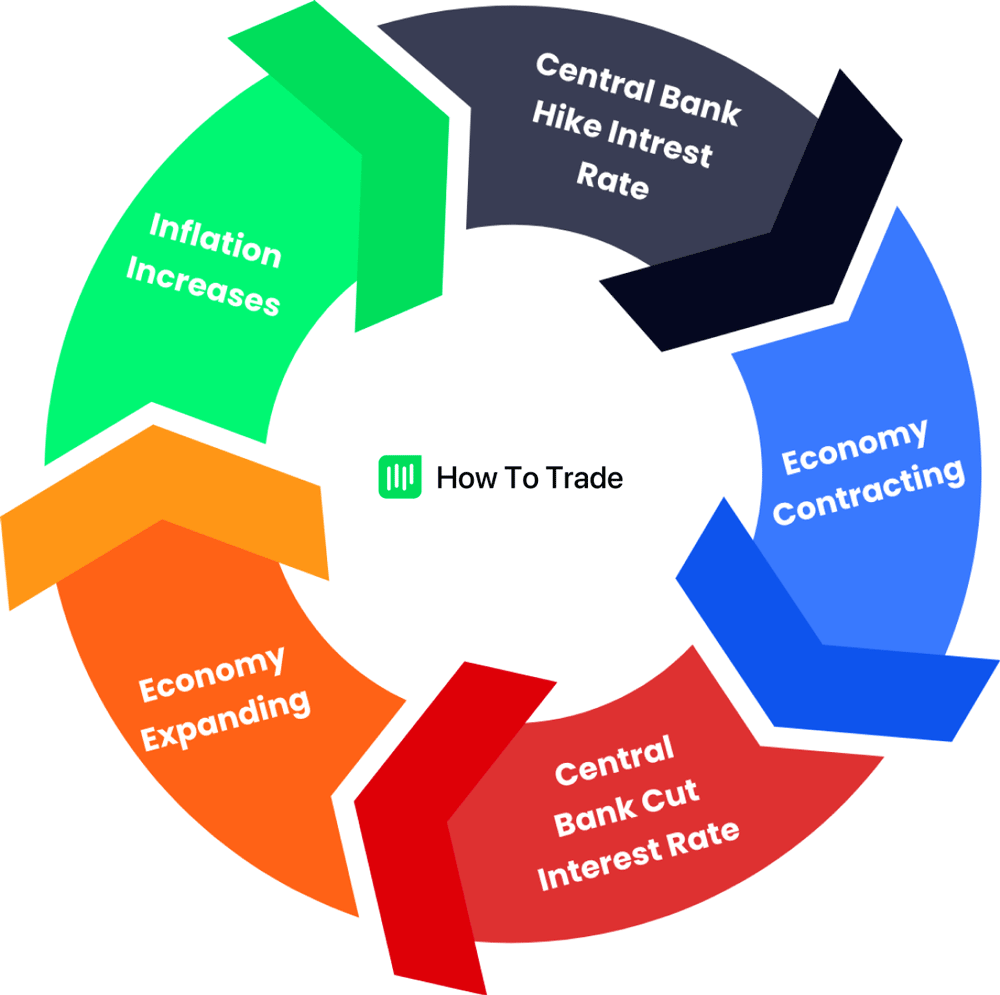
Inflation is a significant factor to consider in any study of the global capital markets. And, like unemployment, central banks are tasked with ensuring pricing stability. Authorities like the Fed or BoE raise interest rates and limit credit availability to keep inflation in check.
Generally, the domestic currency appreciates when central banks attack inflation by raising interest rates. So, when the Fed hikes rates, the USD is positioned to rally across the currency markets. Why? Because people are incentivized to deposit money and refrain from borrowing.
Forex Macroeconomics Trading Strategies
Macroeconomics is a crucial element of fundamental analysis. Accordingly, there are countless fundamental trading strategies based on this area of study. Below are two:
- Trading economic reports: The release of official metrics such as GDP or Non-Farm Payrolls typically brings enhanced market volatility. Amid such releases, many forex traders buy or sell currency pairs in reaction to the hard data. Also, technical momentum, trend, or reversal strategies are frequently applied to the enhanced price action.
- Cyclical Trading: During periods of economic uncertainty, forex players often take positions based on what they believe central banks will do. For instance, during an explosive U.K. economic activity and inflation period, a trader may buy the GBP in anticipation of the BoE hiking interest rates.
Remember, there are many ways to make money in the forex markets. The foreign exchange strategies above are only the tip of the iceberg!

How to Enhance Your Forex Performance Using Macroeconomics
As with any strategy or discipline, there are a few things that you must do to make macroeconomic analysis work for you. Two of the most important are to think forex and be consistent.
1. Think Forex
It doesn’t help to become an expert on international trade if you don’t understand how it impacts exchange rates. All the macroeconomic data in the world is useless if you can’t apply it to the foreign exchange market. That’s why it’s critical that you not only digest financial information but always ask the question, “How will this information impact the forex?”
Before diving into an economic release or a country’s financials, think about how the data set can impact that country’s currency. For instance, if you’re trading the Canadian dollar (CAD), it helps to have at least a basic understanding of Canada’s key imports, exports, goods, and services. If not, the economic information can quickly become “number soup.”
2. Be Consistent
Regardless of analysis or strategy, you must be consistent with your methodology. This also applies to the study of macroeconomics. If your research varies from currency pair to currency pair, it will become challenging to understand the “whys” behind exchange rate fluctuations.
At this point, you may be wondering how to stay consistent with macroeconomic analysis. One way is always to compare apples to apples. If you compare Zimbabwe’s GDP to U.K. unemployment when trading the GBP/ZWD, your analysis is inherently flawed. Here’s why:
- For starters, Zimbabwe is an emerging economy, and the U.K. is developed. Thus, comparing GDP levels is relatively futile.
- Second, GDP is an economic growth measure; unemployment is a labor-centric metric.
- Third, the comparison completely ignores ZWD currency pegs and the hyperinflationary challenges faced by Zimbabwe.
Key Takeaways
- Macroeconomics studies the performance of an economy based on three factors: economic output, unemployment, and inflation.
- These three have a huge bearing on the market because they directly affect economies, which in turn affect the value of currencies.
- One way to involve the knowledge of macroeconomics in trading is through news trading.
Wrapping Up
One of the most potent tools forex traders worldwide use is macroeconomic analysis. Studying market drivers such as inflation, unemployment, and industrial growth can give us invaluable insights into exchange rate fluctuations.
However, when you conduct your analysis, remember to do two things: think forex and compare apples to apples. By doing so, you can apply what you have learned and consistently cash in on differences in exchange rates!
Macroeconomics is only one facet of fundamental analysis. Move on to the next lesson to learn more about forex fundamentals and how they impact currency exchange rates.

